We present photometric and spectroscopic observations of the members of three previously cataloged compact group (CG) candidatesat redshifts $z>0.3$. These confirm spectroscopic redshifts compatiblewith being gravitationally bound structures at redshifts 0.3112, 0.3848and 0.3643 respectively, and then they are the most distant CGs known with spectroscopic confirmation for all their members. The morphological and spectroscopic properties of all their galaxies indicate early types dominated by an old population of stars, with little star formation or nuclear activity. Most of the physical properties derived for the three groups are quite similar to the average properties of CGs at lower redshifts. In particular, from the velocities and positions of the respective members of each CG, we estimate short dynamic times. These leave open the questions of identifying the mechanism for forming CGs continuously and the nature of the final stages of these structures.
Advertised on
References
It may interest you
-
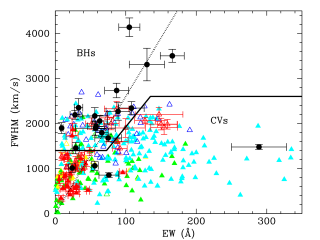 Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on
Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on -
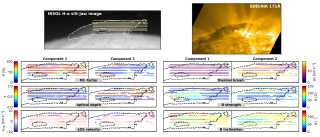
 The solar corona—the outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere—is extremely hot and very low in density. One of the main challenges in solar physics is understanding why the corona reaches temperatures of over a million degrees. This heating is believed to be closely related to the Sun’s magnetic field. However, quantifying the coronal magnetic field is difficult because the light emitted by the corona is extremely faint, and its polarization signals, which encode the information on the magnetic field, are subtle. Thanks to recent advances in technology, telescopes like the Daniel K. InouyeAdvertised on
The solar corona—the outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere—is extremely hot and very low in density. One of the main challenges in solar physics is understanding why the corona reaches temperatures of over a million degrees. This heating is believed to be closely related to the Sun’s magnetic field. However, quantifying the coronal magnetic field is difficult because the light emitted by the corona is extremely faint, and its polarization signals, which encode the information on the magnetic field, are subtle. Thanks to recent advances in technology, telescopes like the Daniel K. InouyeAdvertised on -
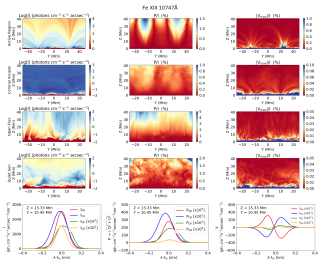
 Understanding the magnetic field in the corona is key for explaining the fascinating physical processes occurring there. However, the extreme conditions in the outer solar atmosphere hamper the possibility of acquiring observations with enough quality to infer the coronal magnetic field. Analyzing observations of overdensities of cold plasma supported by coronal magnetic fields, including filaments and prominences, allows us to understand such magnetic fields and their interaction with plasma. In this study, we have analyzed an active region prominence, a type of prominence that has barelyAdvertised on
Understanding the magnetic field in the corona is key for explaining the fascinating physical processes occurring there. However, the extreme conditions in the outer solar atmosphere hamper the possibility of acquiring observations with enough quality to infer the coronal magnetic field. Analyzing observations of overdensities of cold plasma supported by coronal magnetic fields, including filaments and prominences, allows us to understand such magnetic fields and their interaction with plasma. In this study, we have analyzed an active region prominence, a type of prominence that has barelyAdvertised on