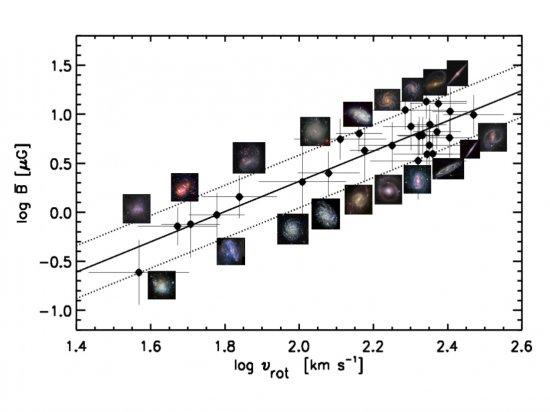
Magnetic fields are present on all scales in the Universe from planets and stars to galaxies and galaxy clusters, and even at high redshifts. They are important for the continuation of life on the Earth, the onset of star formation, the order of the interstellar medium, and the evolution of galaxies. Hence, understanding the Universe without understanding magnetic fields is impossible. The origin and evolution of cosmic magnetic fields is among the most pressing questions in modern astronomy. The most widely accepted theory to explain the magnetic fields on stars and planets is the α-Ω dynamo theory. This describes the process through which a rotating, convecting, and electrically conducting fluid can maintain a magnetic field over astronomical timescales. On larger scales, a similar dynamo process could produce coherent magnetic fields in galaxies due to the combined action of helical turbulence and differential rotation, but observational evidence for the theory is so far very scarce. Putting together the available data of non-interacting, non-cluster galaxies with known large-scale magnetic fields, we find a tight correlation between the strength of the large-scale magnetic field and the rotation speed of galaxies. This correlation is linear assuming that the number of cosmic-ray electrons is proportional to the star formation rate, and super-linear assuming equipartition between magnetic fields and cosmic rays. This correlation cannot be attributed to an active linear α-Ω dynamo, as no correlation holds with global shear or angular speed. It indicates instead a coupling between the large-scale magnetic field and the dynamical mass of the galaxies. Hence, faster rotating and/or more massive galaxies have stronger large-scale magnetic fields. The observed correlation shows that the anisotropic turbulent magnetic field dominates the large-scale field in fast rotating galaxies as the turbulent magnetic field, coupled with gas, is enhanced and ordered due to the strong gas compression and/or local shear in these systems. This study supports a stationary condition for the large-scale magnetic field as long as the dynamical mass of galaxies is constant.
Advertised on
References
It may interest you
-
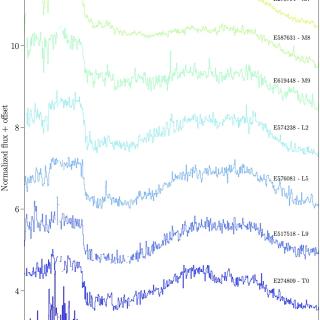 The Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) on board the Euclid space mission has obtained near-infrared (NIR) spectra of millions of objects, including hundreds of ultracool dwarfs (UCDs). Euclid observations retrieve images and slitless spectra simultaneously. This observing mode marks a new era in the discovery of new objects, such as L- and T-type dwarfs, which can be found from direct identification through the H2O and CH4 absorption bands. NISP spectral resolution (R ∼ 450) is enough to classify the objects by the spectral type using known standard templates. Q1 provided moreAdvertised on
The Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) on board the Euclid space mission has obtained near-infrared (NIR) spectra of millions of objects, including hundreds of ultracool dwarfs (UCDs). Euclid observations retrieve images and slitless spectra simultaneously. This observing mode marks a new era in the discovery of new objects, such as L- and T-type dwarfs, which can be found from direct identification through the H2O and CH4 absorption bands. NISP spectral resolution (R ∼ 450) is enough to classify the objects by the spectral type using known standard templates. Q1 provided moreAdvertised on -
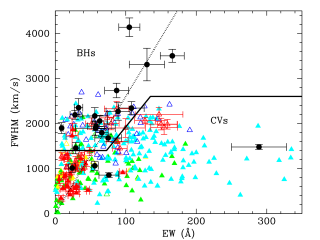 Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on
Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on -
 O ne of the key challenges in astronomy is to measure accurate distances to celestial objects. Knowing distances is crucial since it allows us to measure physical properties such as size, mass and luminosity. Since we can’t go out and use a tape-measure, a range of different approaches have been developed. Many of these approaches rely on using “standard candles”. Standard candles are objects (for example stars or supernovae) for which we know their intrinsic ”true” brightness. Once we know this, then their observed brightness compared to their intrinsic brightness gives us a distance to theAdvertised on
O ne of the key challenges in astronomy is to measure accurate distances to celestial objects. Knowing distances is crucial since it allows us to measure physical properties such as size, mass and luminosity. Since we can’t go out and use a tape-measure, a range of different approaches have been developed. Many of these approaches rely on using “standard candles”. Standard candles are objects (for example stars or supernovae) for which we know their intrinsic ”true” brightness. Once we know this, then their observed brightness compared to their intrinsic brightness gives us a distance to theAdvertised on