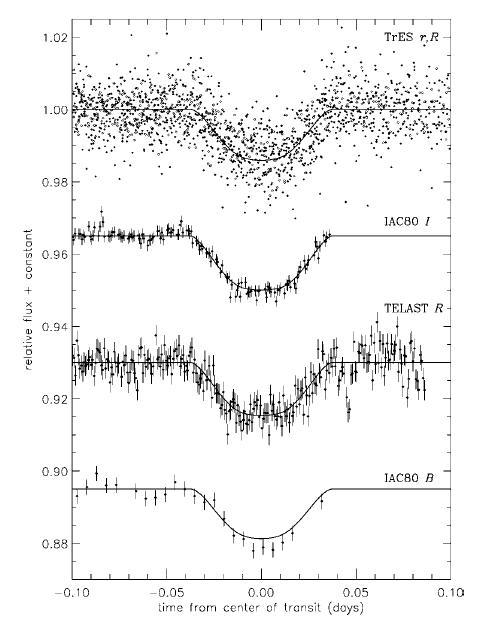
In August 2006 a new planetary transit was discovered from data from the TrES network. The discovery was confirmed using radial velocity curves obtained with the Keck and characterised with light curves in different filters obtained using two telescopes at the Observatorio del Teide: "IAC80" and "TELAST" (the first result of scientific interest obtained from the latter). The planet discovered, TrES-2, is more massive and somewhat larger than its quasi-homonym TrES-1 (the first exoplanet discovered using the transit method), and follows the expected patterns for this type of object. Its main importance is that it is the first object discovered in the area of observation of the future Kepler satellite, which will be able to track it in a degree of detail never before achieved.
Light curves of TRES_2 obtained using telescopes of the network and with two telescopes from the Observatorio del Teide: "IAC-80" and "TELAST" with different filters.
Advertised on